On this page
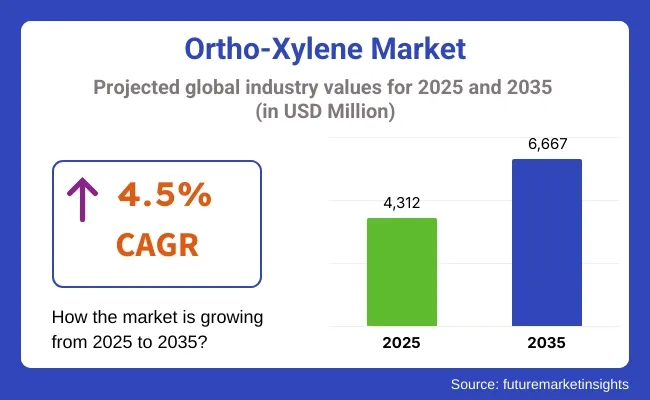
Global ortho xylene production in 2026 is estimated at approximately 3 to 4 million tonnes, reflecting its role as a key aromatic intermediate primarily consumed in phthalic anhydride production. Output trends closely follow operating rates in aromatics complexes and downstream demand from plasticisers, resins and unsaturated polyester applications.
Production economics are driven by reformate availability, mixed xylene pool composition, separation efficiency and energy intensity of fractionation. Cost behaviour is strongly influenced by the relative balance among ortho, meta and para xylene streams, since separation decisions affect overall aromatics optimisation rather than ortho xylene alone.
The global supply environment shows disciplined capacity management rather than rapid expansion. Incremental improvements focus on recovery efficiency, debottlenecking of fractionation units and integration with downstream phthalic anhydride assets. Large scale standalone capacity additions remain limited due to high capital intensity and feedstock integration requirements.
Production capacity is concentrated in regions with large scale refining and petrochemical infrastructure. Asia Pacific leads global output supported by integrated aromatics complexes and downstream chemical consumption. Europe maintains stable capacity aligned with plasticiser and resin demand. North America supports meaningful production integrated with refinery reformers and chemical manufacturing. Several regions rely on imports due to limited aromatics separation capability.
Phthalic anhydride production continues to anchor baseline demand, with additional consumption in coatings resins, plasticisers and specialty intermediates. Buyers value consistent purity, predictable supply and alignment with downstream operating schedules.
The majority of ortho xylene is consumed captively or under contract by phthalic anhydride producers. Direct use as a solvent is limited and highly application specific. Buyers differentiate supply based on isomer purity, sulfur content and trace impurity control.
Ortho xylene is recovered from mixed xylene streams rather than produced independently. Separation efficiency and energy management are central operational challenges. Integration with downstream consumption improves overall system economics and reduces logistics exposure.
Phthalic anhydride production dominates volume consumption due to continuous operating requirements. Resin and specialty chemical uses contribute smaller volumes but introduce additional purity and scheduling constraints. Buyers focus on steady supply, predictable composition and long term availability.
Asia Pacific leads global ortho xylene production supported by large scale refining capacity and downstream phthalic anhydride integration.
Europe maintains stable production aligned with plasticiser and resin manufacturing, with limited scope for capacity expansion.
North America supports integrated production tied to refinery reformers and chemical complexes.
Other regions depend on imports due to limited aromatics separation infrastructure and smaller refining footprints.
The supply chain begins with crude oil processing followed by catalytic reforming, aromatics extraction, xylene separation, storage and distribution. Downstream buyers include phthalic anhydride producers, resin manufacturers and specialty chemical producers.
Key cost drivers include crude feedstock quality, reformer operating severity, energy use in fractionation and logistics. Storage and transport costs are moderate but influenced by flammability classification and handling requirements. Trade flows reflect concentration of production in refining hubs supplying downstream chemical regions.
Pricing formation reflects feedstock economics, energy intensity and contract structure rather than short term volatility.
The ecosystem includes refiners, aromatics producers, fractionation operators, phthalic anhydride manufacturers, resin producers and regulators. Production decisions are often optimised at the aromatics pool level rather than for ortho xylene alone.
Equipment suppliers support reformers, extractive distillation units, fractionation columns and storage systems. Producers coordinate crude selection, operating severity, downstream integration and long term supply arrangements.
Global production in 2026 is estimated at approximately 3 to 4 million tonnes, largely driven by phthalic anhydride demand.
Costs are driven by crude feedstock quality, reformer operation, energy use in separation and logistics.
It is recovered from mixed xylene streams, and production decisions are governed by overall aromatics optimisation.
Buyers rely on integrated supply, inventory buffers and long term agreements aligned with downstream unit operation.
Explore Hydrocarbons, Petrochemicals, and Organic Chemicals Insights
View Reports
Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.